What is Application Portfolio Rationalization and what are the key drivers and steps within rationalization?
Application portfolio rationalization is an assessment and analysis of an organization’s portfolio of IT applications on various parameters that define the future strategic roadmap for the application portfolio.
An IT organization’s application portfolio usually grows over the years due to multiple changing business needs, mergers and acquisitions etc. For many organizations, this has resulted in a complex web of legacy applications which not only attract high maintenance and support costs, but also lack the flexibility and speed to adapt to changing business needs.
The enormous growth of digitization in terms of Social, Mobility, Analytics and Cloud have led to significant disruptions to organizations’ time-tested business models. The increased competition to acquire and retain market share has made it necessary for organizations to improve their market outreach and improve user experience through seamless multichannel interactions and faster rollout of more tailored products in the market.
To avail the full benefits of digitization, more and more organizations are adopting the ‘Cloud First’ approach and migrating their existing applications to cloud through various IaaS, PaaS and SaaS based solutions. Organizations are also moving from monolithic applications to microservices-based composable architecture, bringing in agile DevOps practices and implementing continuous integration and continuous deployments for incremental rollout of product features in the market.
The growth of digitization and cloud has made it imperative for organizations to relook at their application portfolio and transform their application portfolio to a more nimble, responsive and future-ready IT landscape. This is where an efficient application portfolio rationalization can play a key role in attaining business objectives.
Primary drivers for Application Portfolio Rationalization
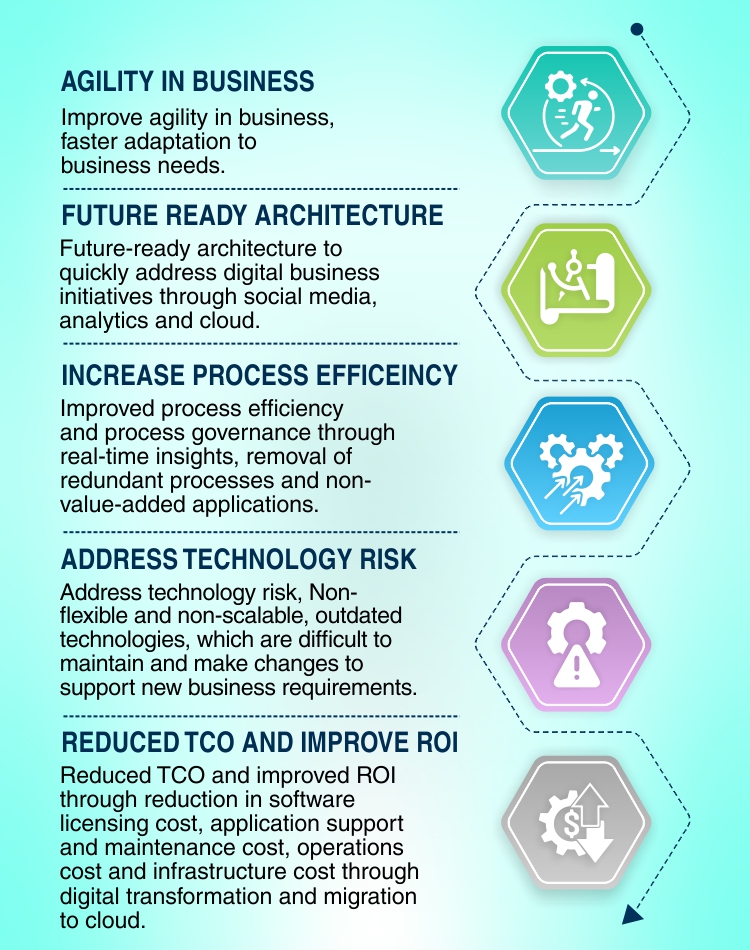
An overview of the phases within Application Portfolio Rationalization are as follows:

Key steps within application portfolio rationalization:
Application Inventory Analysis
Gather data throughout your organization to create a well-defined vetted inventory of applications with application owners. Classify applications as ‘System of Record, System of Differentiation and Systems of Innovation’ as recommended in Gartner’s Pace-Layered analysis of applications. It has been observed that aligning application portfolios to Gartner’s Pace-Layered strategy helps to deliver faster response to business demands and increase ROI.
Business Capability and Process Alignment of Applications
Assess business alignment of applications. Map each application within the portfolio to level-1 and level-2 business capabilities and level-1 and level-2 business processes they support. A detailed mapping of application to business capability and processes helps to analyze redundancies within applications, parallel processes run across applications, and provides opportunities for consolidation.
Assess Functional Quality of Applications
Assess applications based on criticality of the business processes they support, business process coverage, integration and interfaces of the application, ability of the application to support future business needs, and readiness of the applications to conform to compliance and regulatory requirements.
Assess Technical Quality of Applications
Assess an application based on how well it meets technology standards, for how long its technology version is supported, ease of making changes to the application, and whether the application has a future-ready architecture to quickly adapt to the changing business requirements. Assess maintainability, modularity, scalability, reliability, and digital alignment of the application.
Assess Operational Quality of Applications
Assess operational excellence of an application in terms of frequency of changes required, ability to meet the desired service levels, whether the application is able to meet the required compliance and regulatory requirements, business continuity and disaster recovery considerations for the application.
Assess TCO and ROI of Applications
Assess total cost of ownership for applications. This should include all types of costs incurred on the application, such as infrastructure and operation cost, software licensing cost, licensed software support cost, application break fix and run cost and cost of enhancements as required in the application. Assess total ROI as well as direct and indirect revenue from the application.
Define Roadmap Phase
To define the future roadmap for the application portfolio, inputs are taken from applications’ business capability and process map, application’s functional complexity and alignment, applications’ technical complexity and alignment, applications’ operational excellence and complexity, and total TCO and ROI of the applications. Additionally, an organization’s business priorities and strategy, short-term and long-term goals are assessed to arrive at the final plan for consolidation and simplification of the application portfolio. Decisions on application rationalization and roadmap planning need to focus on reducing redundancies, improving efficiencies, reducing support and maintenance costs, and making the application portfolio future ready to quickly adapt to changing business and market needs. By following this roadmap, your organization should be able to reduce the number of applications as well as total inventory of infrastructure and management resources.
If done correctly with proper rigor and planning, application portfolio rationalization and a well-defined future-state roadmap for the portfolio can bring significant business benefits and agility for an organization’s business. It can help the organization to quickly align to industry-leading business and technology perspectives and respond to the digital disruptions impacting the market.
This is an introductory blog on Application Portfolio rationalization and aims to provide the key drivers and steps within rationalization. There will be subsequent blogs which will explain each area within rationalization in more detail.
In my next blog, I will be talking in detail about Gartner’s Pace-Layered analysis of applications. So stay tuned for more…
References:
http://www.gartner.com/it-glossary/pace-layered-application-strategy/



